Home » Design Technology

DFMEA is a structured engineering methodology to identify potential failures in design and mitigate risks before production.
Module 1: FMEA Fundamentals
Module 2: Failure Mode Identification Techniques
Module 3: Severity, Occurrence, Detection Ratings
Module 4: RPN Calculation
Module 5: Criticality & Risk Prioritization
Module 6: Recommended Actions
Module 7: DFMEA Templates & Case Studies
Module 8: Best Practices in Automotive & Aerospace

PFMEA ensures manufacturing processes are robust, safe, and optimized for quality and efficiency.
Module 1: Introduction to PFMEA
Module 2: Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Module 3: Failure Mode Analysis
Module 4: Severity, Occurrence, Detection
Module 5: Control Plan Development
Module 6: Corrective Actions
Module 7: PFMEA Documentation & Auditing
Module 8: Industry Case Studies
Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL), Software-in-the-loop (SIL), and Model-in-the-loop (MIL) simulations validate embedded systems before real hardware deployment.
Module 1: Control Systems Overview
Module 2: Introduction to MIL, SIL, and HIL
Module 3: Simulink-Based Controller Modeling
Module 4: Real-Time Simulation Tools (dSPACE, NI)
Module 5: Code Generation using Embedded Coder
Module 6: Plant Modeling
Module 7: Test Automation & Validation
Module 8: Real-World Case Studies (Automotive/Robotics)
GD&T standardizes how engineers define tolerances, shapes, and allowable variations on engineering drawings to ensure manufacturability.
Module 1: Introduction to ASME Y14.5
Module 2: Datum Systems
Module 3: Form, Orientation, Location, and Runout Symbols
Module 4: Tolerance Zones
Module 5: Feature Control Frames
Module 6: Basic Dimensions
Module 7: Inspection Methods
Module 8: Practical Case Studies
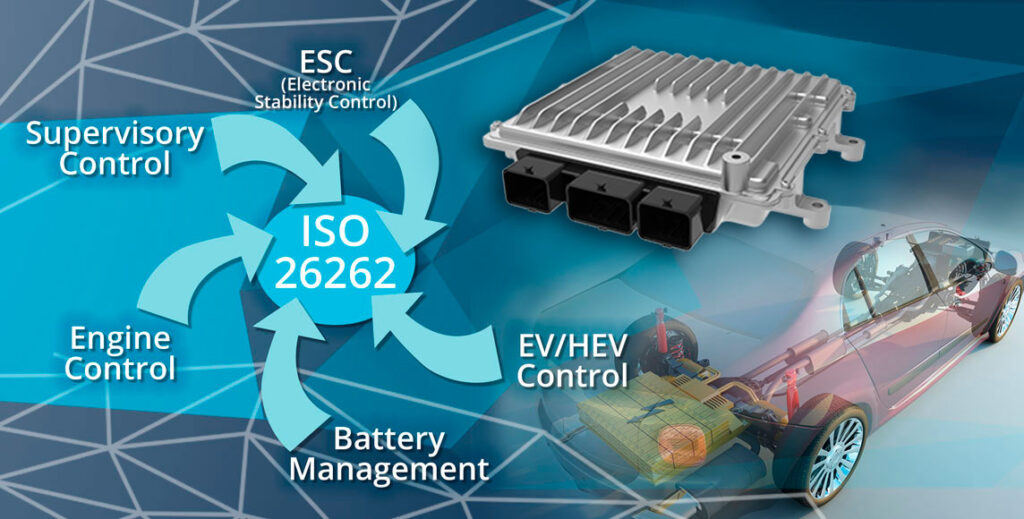
Functional Safety ensures electronic systems operate safely even during faults, primarily focused on automotive electronics under ISO 26262.
Module 1: Functional Safety Fundamentals
Module 2: ISO 26262 Framework
Module 3: HARA (Hazard Analysis & Risk Assessment)
Module 4: ASIL Levels & Safety Goals
Module 5: Safety Lifecycle & V-Model
Module 6: Safety Mechanisms & Architecture
Module 7: Software & Hardware Safety
Module 8: Safety Case Development
Module 9: Industry Projects (EV/ADAS)
we are formally known as Headwaters Training Consultants Pvt. Ltd. PROPUPIL empowers growth through tailored solutions that boost leadership, performance, and strategic alignment.
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved By PROPUPIL Learning Consultants. Designed by Digju.com